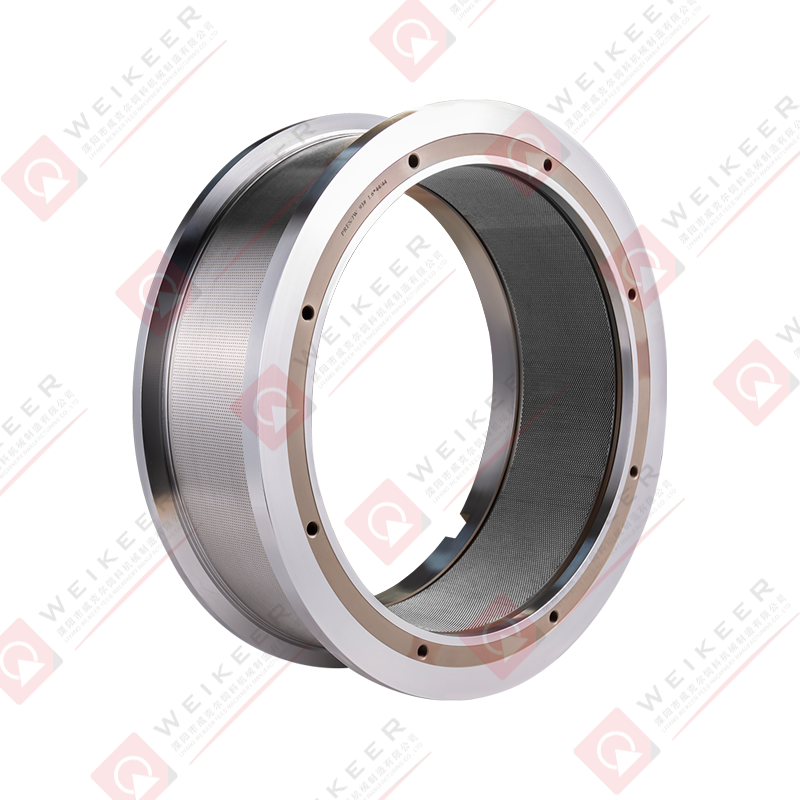
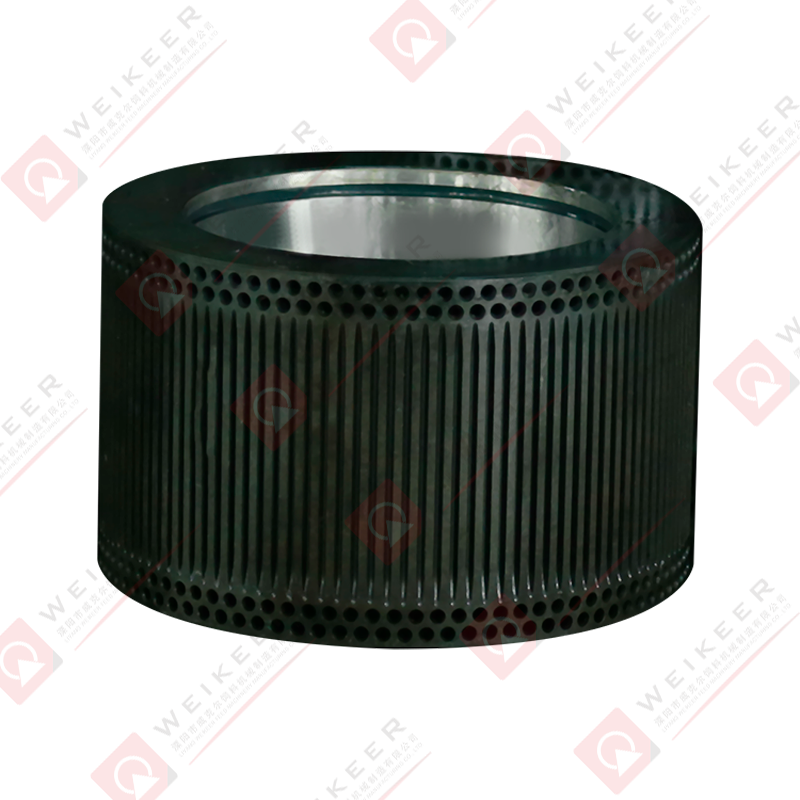
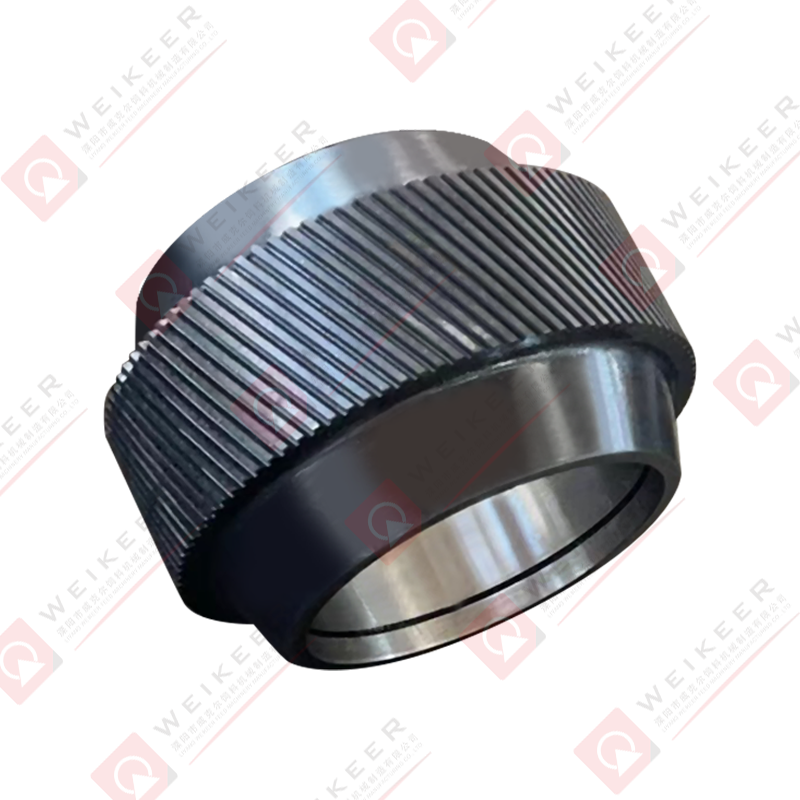
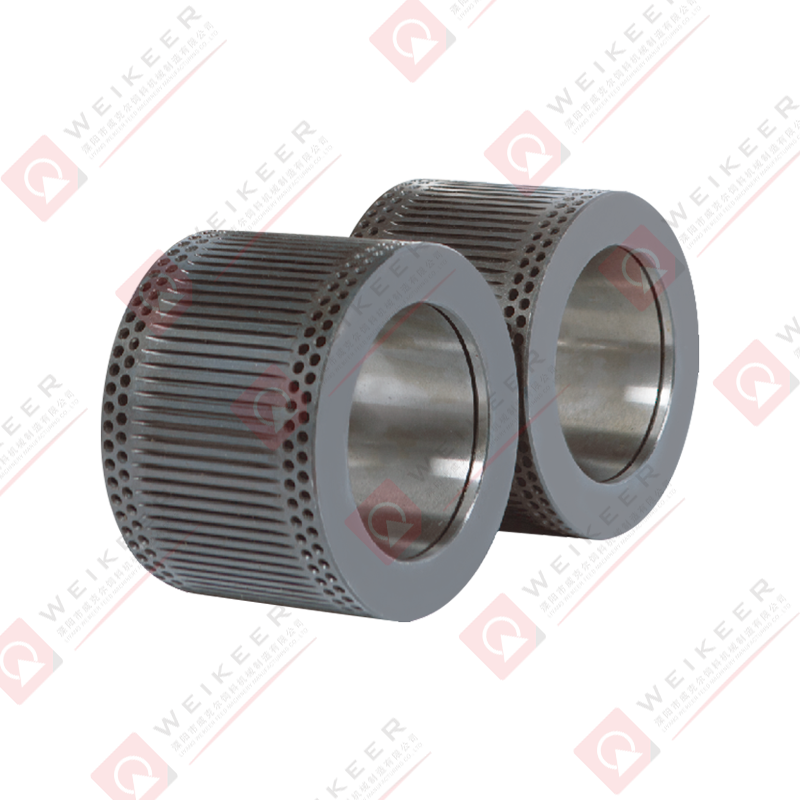
In the world of biomass fuel production, feed processing, and wood pellet manufacturing, pellet mills are the cornerstone of productivity and efficiency. Among their key components, the ring die stands out as the heart of the pelletizing process. One of the most efficient and long-lasting innovations in this space is the screw type stainless steel ring die. But what exactly is it, and why is it gaining popularity in modern pellet mill operations?
This article explores the structure, function, benefits, applications, and considerations of the screw type stainless steel ring die. Whether you're an industry professional, equipment supplier, or someone new to pellet production, understanding this component can help improve your output quality, operational stability, and cost-effectiveness.
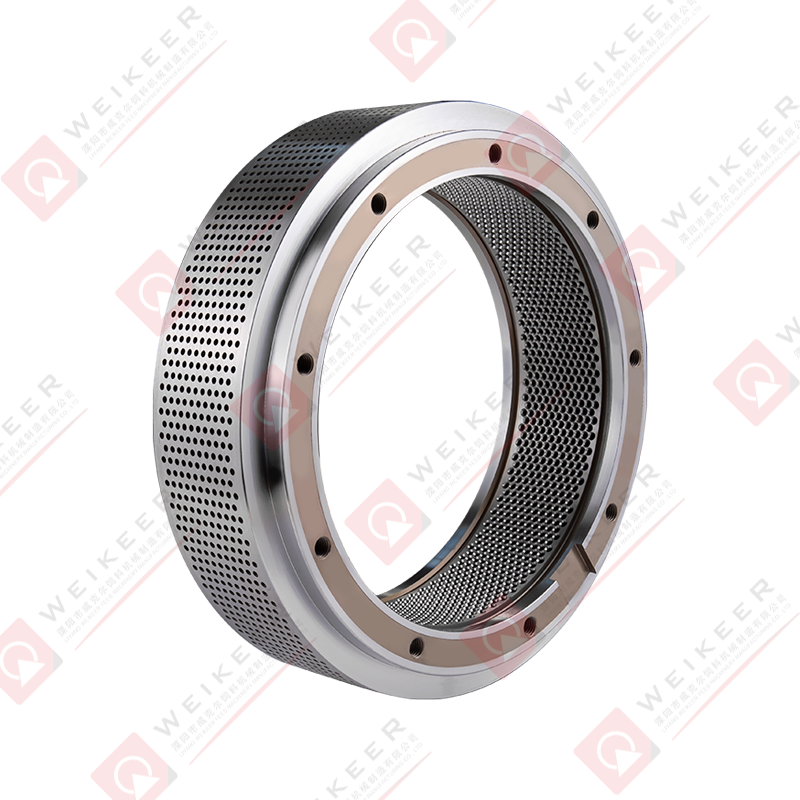
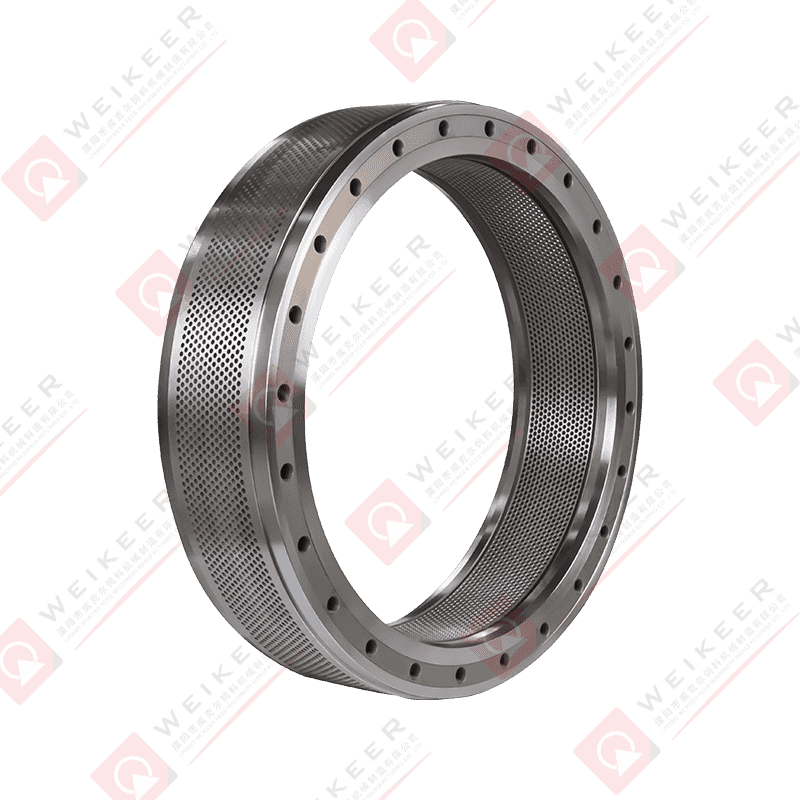
What Is a Screw Type Stainless Steel Ring Die?
A screw type stainless steel ring die is a precision-engineered circular metal component used in ring die pellet mills. It is responsible for forming raw powdered materials—such as wood chips, sawdust, straw, feed, or biomass—into compact pellets by forcing them through cylindrical die holes.
The term “screw type” refers to the mechanical locking or fastening structure between the ring die and the mill, usually involving threaded bolts or a screw clamping mechanism. This design improves installation stability and ensures consistent pressure during operation.
The term “stainless steel” highlights the material used—corrosion-resistant, high-strength alloys like SS304, SS316, or martensitic stainless steel—chosen for their excellent wear resistance, heat tolerance, and hygienic properties.
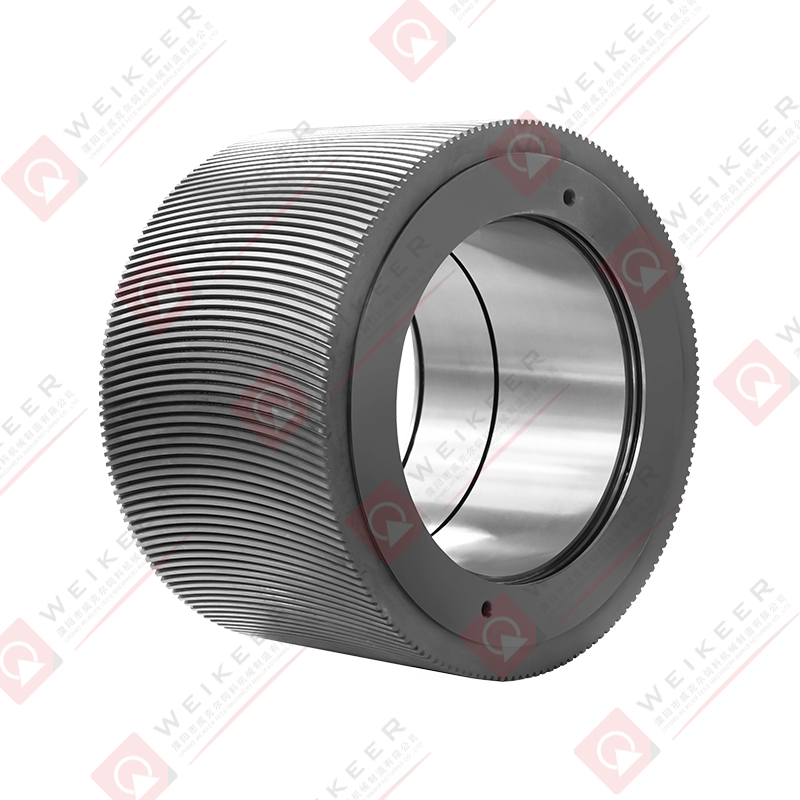
How Does a Ring Die Work in a Pellet Mill?
In a ring die pellet mill, raw material is fed into the machine’s conditioning chamber, where it is softened with steam or moisture. Then, it enters the die chamber:
1. Rollers press the softened material against the inner surface of the ring die.
2. The material is forced through die holes, forming cylindrical pellets.
3. Knives cut the extruded pellets to desired lengths as they exit.
The ring die must endure high pressure, friction, and temperature during this process. Its precise hole size, pattern, and surface finish all contribute to the efficiency, quality, and consistency of pellet production.
Why Choose a Screw Type Design?
The screw-type fastening mechanism offers several advantages over conventional clamp or bolt-lock systems:
Stronger and safer installation: The threaded design holds the die more securely during high-torque operation.
Better alignment: Reduces vibration and ensures even pressure distribution across the die surface.
Easier maintenance and die replacement: Screws allow for quicker disassembly and reinstallation, reducing downtime.
Reduced mechanical stress: Prevents shifting or loosening of the die during continuous operation, which can otherwise lead to poor pellet quality.
This makes the screw type ring die especially valuable in high-output industrial pellet mills, where operational reliability and production continuity are critical.
Why Is Stainless Steel Used in Ring Dies?
The choice of stainless steel for ring dies is based on a range of performance-enhancing characteristics:
1. Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel resists oxidation, moisture, and chemical reactions, which is particularly useful when processing acidic feedstocks or operating in humid conditions.
2. Wear Resistance
Die holes are subjected to constant abrasion. Stainless steel’s surface hardness and toughness prolong the die’s working life.
3. Thermal Stability
Stainless steel maintains structural integrity even at high temperatures generated during the pelletization process.
4. Smooth Surface Finish
High-precision machining of stainless steel allows for smoother pellet extrusion, improving pellet density, durability, and appearance.
5. Sanitary Operation
For food-grade or animal feed pellets, stainless steel ensures compliance with hygiene standards, reducing the risk of contamination.

Key Applications of Screw Type Stainless Steel Ring Dies
These dies are used in a wide variety of industries:
1. Biomass Energy Production
In pelletizing sawdust, rice husk, straw, palm fiber, and other plant waste into biomass fuel pellets, stainless steel dies ensure high throughput and long service life.
2. Animal Feed Industry
In producing livestock feed pellets, the die must withstand aggressive materials like corn, soybean meal, and fish meal. Stainless steel offers the necessary durability and hygiene.
3. Wood Pellet Manufacturing
Hardwood and softwood materials are tough on dies. The high hardness and precision of stainless steel allow for consistent pellet size and density.
4. Fertilizer Pellets
For making organic or compound fertilizer pellets, resistance to chemical corrosion is essential—making stainless steel the ideal choice.
5. Chemical and Plastic Pellets
In some industrial settings, ring dies are used for producing plastic or chemical compound pellets. Here, heat resistance and non-reactivity are essential.
Advantages of Using Screw Type Stainless Steel Ring Dies
Extended Service Life
Stainless steel lasts significantly longer than carbon steel or cast iron dies, especially in abrasive or corrosive environments.
High Efficiency
Precision-drilled holes and smooth inner surfaces enable faster pellet extrusion with lower energy consumption.
Consistent Pellet Quality
Uniform hole sizes and hardness ensure that every pellet meets standard size, density, and moisture specifications.
Reduced Downtime
The screw mounting design makes die replacement or maintenance quicker and easier, keeping production flowing.
Lower Long-Term Costs
Although the initial investment is higher, the reduced wear, lower maintenance, and higher output reduce overall operational costs.
Choosing the Right Ring Die for Your Pellet Mill
When selecting a screw type stainless steel ring die, consider the following factors:
Die Hole Diameter and Compression Ratio: These affect pellet density and must match your material type and final product requirements.
Stainless Steel Grade: SS304 is suitable for general use, while SS316 or martensitic grades offer better wear and heat resistance.
Die Thickness: Thicker dies allow more friction time but increase pressure requirements.
Drilling Pattern: The layout of holes determines pellet output and heat distribution.
Compatibility with Mill Model: The screw configuration and mounting dimensions must match your pellet mill’s design.
Consulting with experienced die manufacturers or your pellet mill supplier can ensure proper selection.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To get the most out of your screw type stainless steel ring die:
Clean regularly to prevent material build-up in die holes.
Lubricate roller-die surfaces to minimize wear.
Monitor temperature and pressure to avoid overloading the die.
Use correct raw material preparation (moisture content, size) for optimal performance.
Inspect for cracking or deformation and replace the die when wear exceeds tolerance.
Proper handling and care will extend die life and keep your pelletizing system running efficiently.
Conclusion
The pellet mills screw type stainless steel ring die represents a convergence of smart design, durable material, and manufacturing precision. It plays a vital role in shaping the efficiency, quality, and profitability of any pellet production process—whether in energy, agriculture, or industry.
By choosing the right ring die, maintaining it correctly, and understanding its performance dynamics, operators can maximize productivity, reduce operational costs, and ensure consistent pellet quality over the long term. As the demand for clean energy, sustainable farming, and industrial efficiency continues to grow, investing in advanced components like stainless steel ring dies will only become more essential.
So, the next time you evaluate your pellet mill setup, remember—the die makes the difference.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体