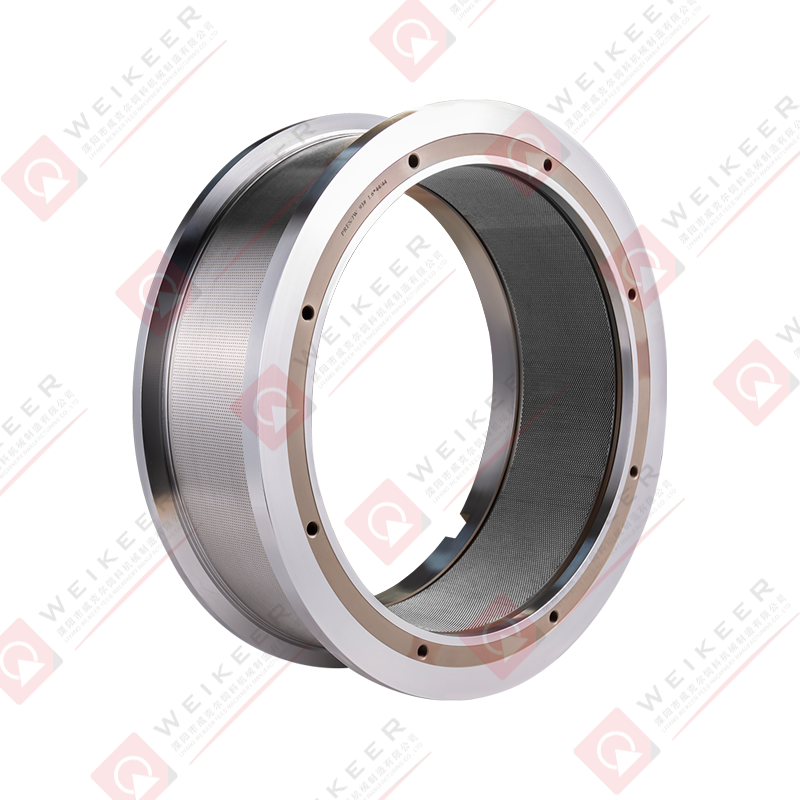
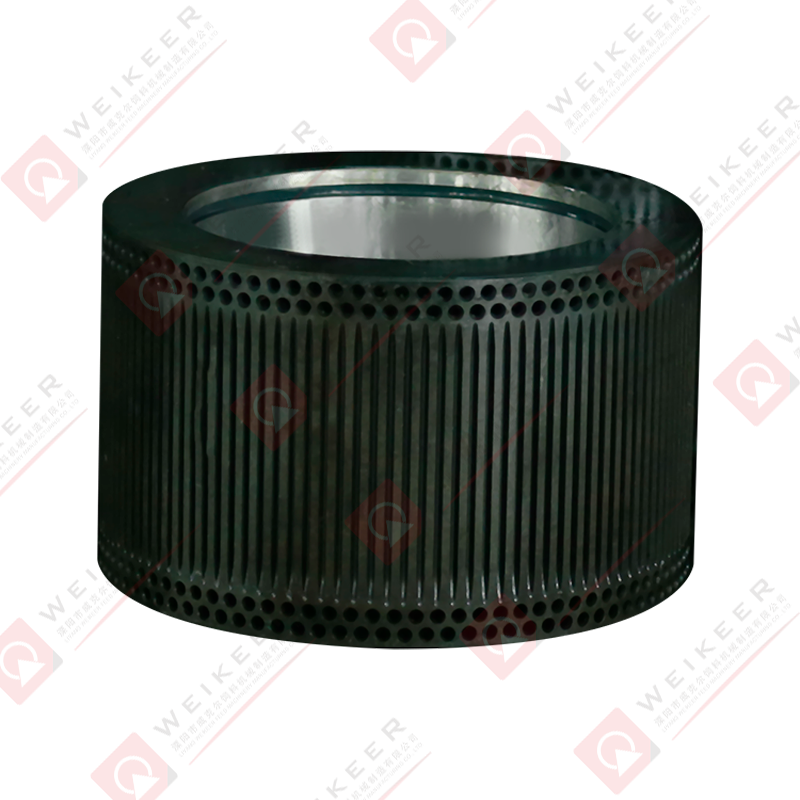
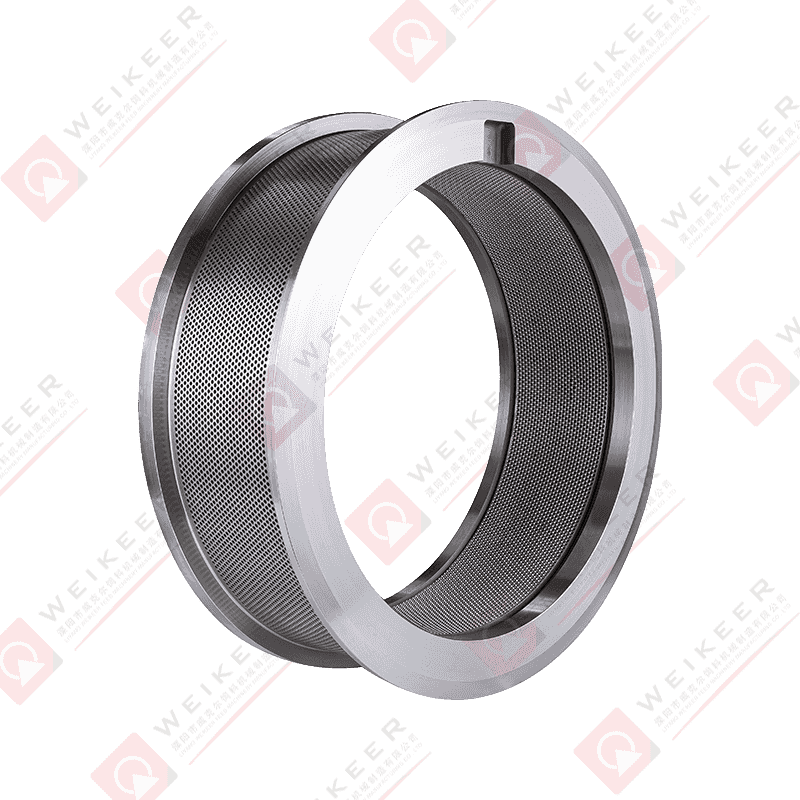
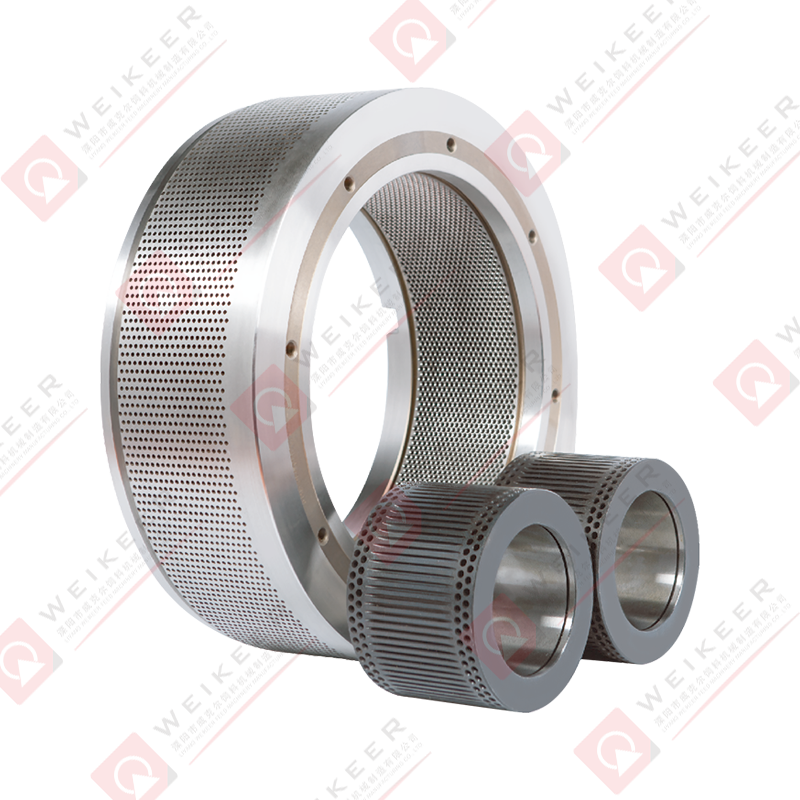
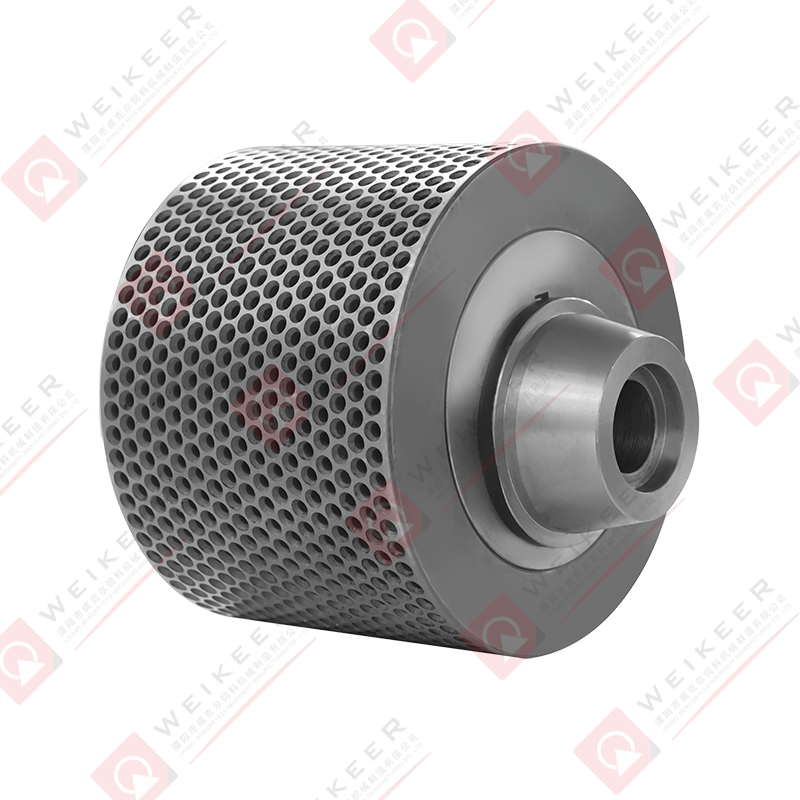
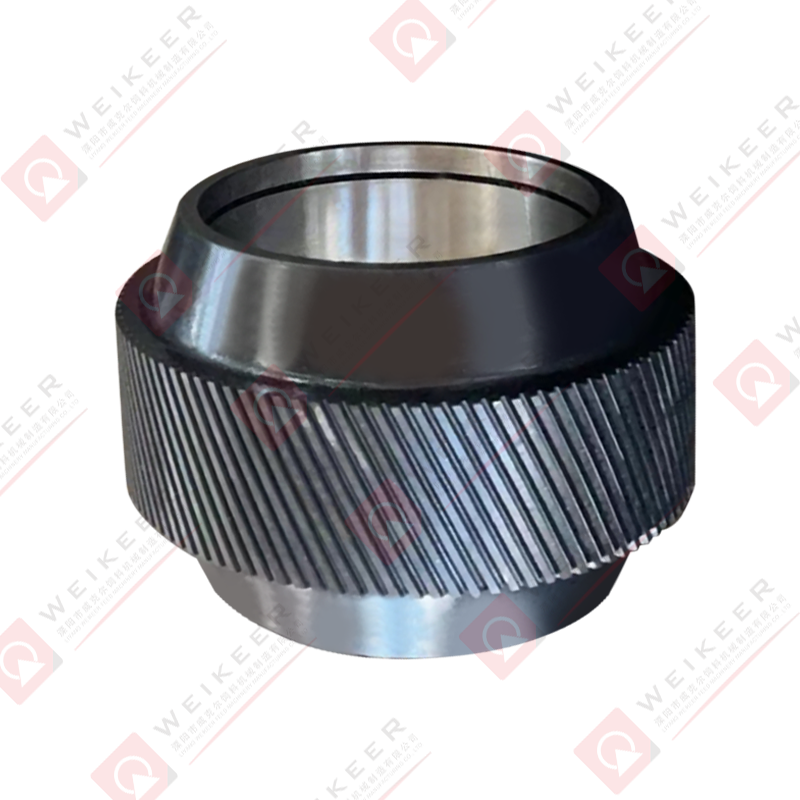
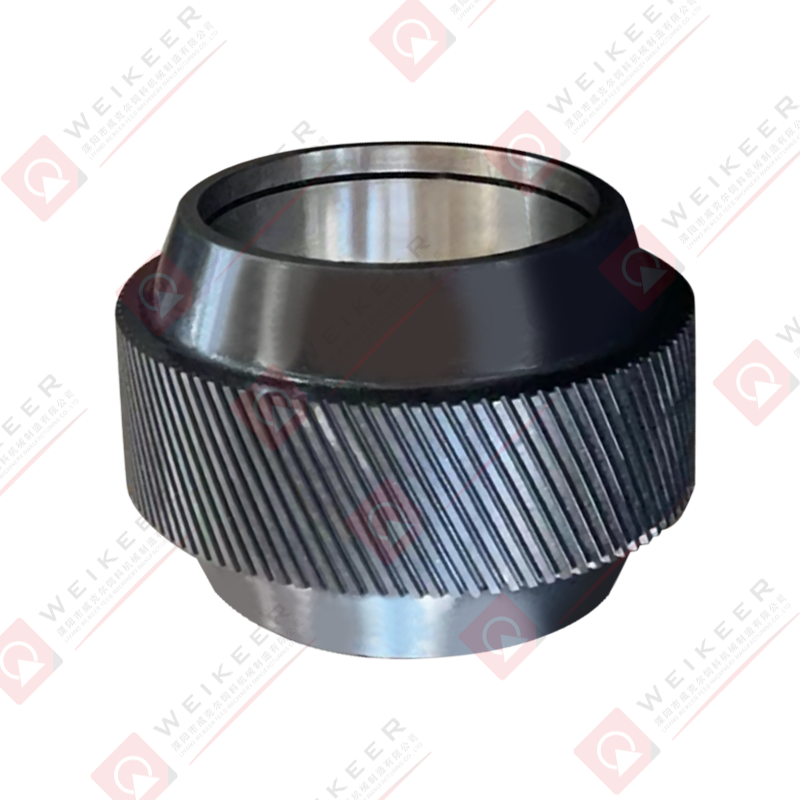
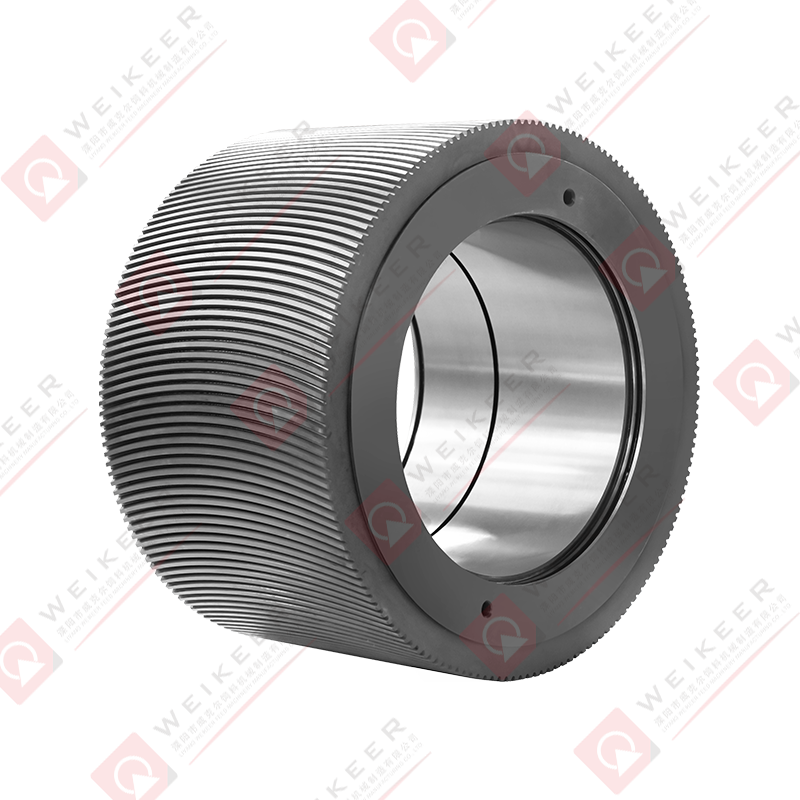
A dimpled bearing steel pellet roller is a critical component used in pelletizing and briquetting systems. Unlike traditional smooth rollers, it features a surface pattern of dimples or depressions that help control material flow, improve grip, and reduce slippage. These rollers are typically made from high-grade bearing steel, such as GCr15 or equivalent, which provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. The dimpled surface is often produced through precise machining or forging, followed by heat treatment and surface finishing to ensure uniformity and durability. The result is a roller that maintains stable performance under high pressure, high speed, and continuous operation conditions.
Key Advantages of Dimpled Bearing Steel Pellet Rollers
The design of a dimpled roller brings several advantages for pellet production. First, the dimples increase surface friction, which helps the roller grab and feed raw material more consistently. This is especially useful for sticky or fine powders that might otherwise slip on a smooth roller. Second, the dimples can reduce the contact area between the roller and material, lowering the tendency for material to build up and cause clogging. Third, the bearing steel core ensures the roller withstands heavy loads and maintains dimensional stability over time. Overall, the combination of surface pattern and material strength results in improved throughput, reduced downtime, and longer service life compared to ordinary rollers.
How Dimple Patterns Affect Pelletizing Performance
The size, depth, and distribution of dimples play a decisive role in how the roller performs. For example, shallow and closely spaced dimples are suitable for materials with good flow properties, as they provide mild grip without aggressive material retention. Deep and widely spaced dimples are better for sticky or moist materials, as they offer stronger anchoring and help release compressed pellets more easily. Engineers often customize dimple patterns based on material characteristics and process parameters, such as moisture content, granule size, and desired pellet density. Proper dimple design can also help reduce roller noise and vibration, contributing to a smoother production line.
Materials and Heat Treatment for Bearing Steel Rollers
Bearing steel is the preferred material for high-performance pellet rollers because it provides a balance of hardness, toughness, and fatigue resistance. Common bearing steel grades used include GCr15, 52100, and equivalent high-carbon chromium alloys. These steels are selected for their ability to achieve high hardness after heat treatment while maintaining sufficient toughness to resist cracking under cyclic loads.
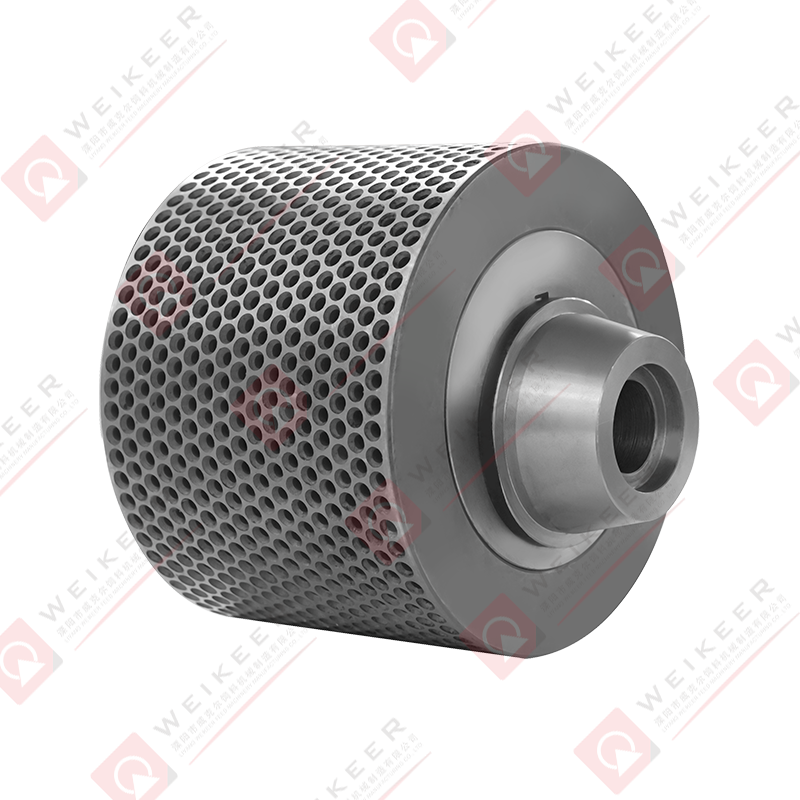
The heat treatment process usually involves quenching and tempering. After forming and machining, the roller is heated to a high temperature to transform its microstructure, then quenched rapidly to lock in a hard martensitic structure. Tempering follows to reduce brittleness and improve toughness. Surface hardening techniques like induction hardening or carburizing may also be applied to enhance wear resistance, especially on the dimpled surface where friction is highest. The final hardness typically ranges between HRC58 and HRC62, depending on the application and material requirements.
Common Applications in Pelletizing and Briquetting
Dimpled bearing steel pellet rollers are widely used in several industrial pelletizing applications. They are commonly found in:
- Biomass pellet mills for wood, straw, and agricultural residues
- Feed pellet machines for livestock and aquaculture
- Metal powder briquetting presses for compacting fine metal powders
- Chemical pelletizing systems for fertilizer and mineral powders
- Plastic pellet production lines where sticky polymer powders need controlled feeding
In each of these applications, the roller’s role is to compress raw material into a dense pellet or briquette. The dimpled surface ensures consistent material capture and reduces slip, while the bearing steel construction withstands continuous pressure and friction without premature wear.
How to Select the Right Dimpled Roller for Your Line
Choosing the right dimpled bearing steel roller requires evaluating both the material properties and the production process. Key selection factors include:
- Material type and moisture content
- Required pellet density and output capacity
- Roller diameter, width, and rotational speed
- Dimple depth, diameter, and spacing
- Heat treatment and surface hardness requirements
- Wear and corrosion resistance needs
A practical approach is to consult with the roller supplier and provide details such as raw material sample, expected throughput, and operating conditions. Many manufacturers can recommend or custom-design the dimple pattern to match your specific process, ensuring stable performance and long service life.
Maintenance Tips for Longer Roller Life
To maximize roller lifespan and prevent unexpected downtime, it is important to implement regular maintenance practices. First, keep the roller surface clean and free from material build-up, which can change the effective dimple pattern and reduce efficiency. Second, monitor bearing lubrication and replace bearings when signs of wear or noise appear. Third, inspect the roller surface for cracks or excessive wear, especially in high-pressure applications.
If the roller shows surface damage, it may be possible to re-machine the dimples or apply a surface coating. However, this should be done carefully to avoid altering the roller’s hardness or dimensional tolerance. In severe cases, replacing the roller may be more cost-effective than repeated repairs.
Comparison Table: Dimpled vs Smooth Rollers
| Feature |
Dimpled Roller |
Smooth Roller |
| Grip on Material |
High |
Medium |
| Material Slip Risk |
Low |
Higher |
| Wear Resistance |
High (with bearing steel) |
Medium |
| Best Use |
Sticky, fine, or difficult materials |
Free-flowing materials |
Conclusion: Why Dimpled Bearing Steel Rollers Are a Smart Investment
Dimpled bearing steel pellet rollers combine the best of design and material engineering to solve common pelletizing challenges. Their patterned surface improves material grip, reduces slippage, and helps prevent clogging, while the bearing steel core ensures high hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. For production lines dealing with sticky powders, high moisture content, or high-pressure compaction, these rollers can significantly improve output stability and reduce maintenance frequency. By selecting the right dimple pattern, heat treatment, and roller size, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency and longer equipment life, making dimpled bearing steel rollers a cost-effective choice for modern pelletizing systems.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体