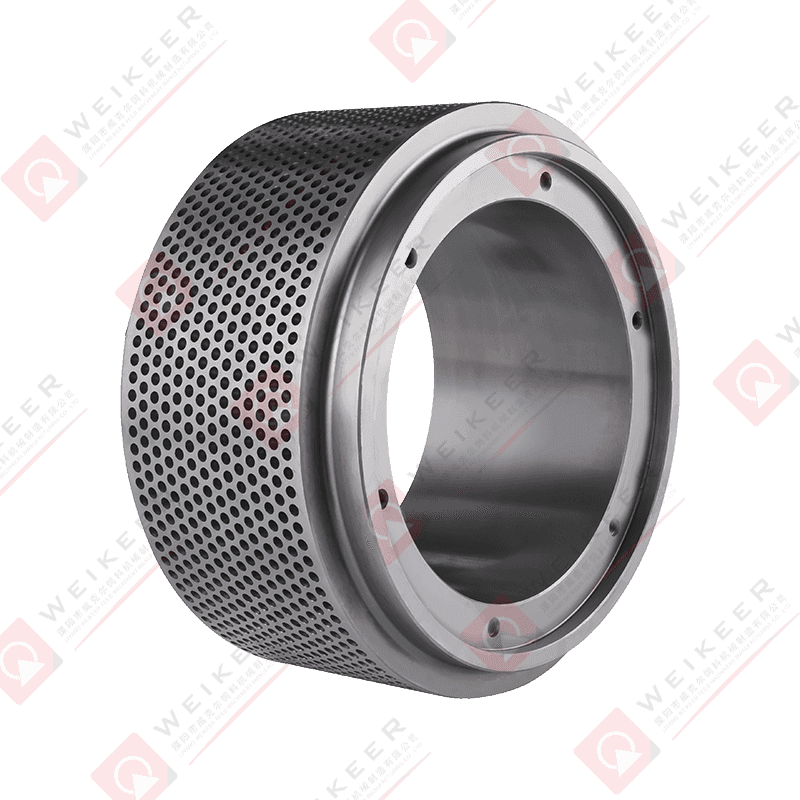
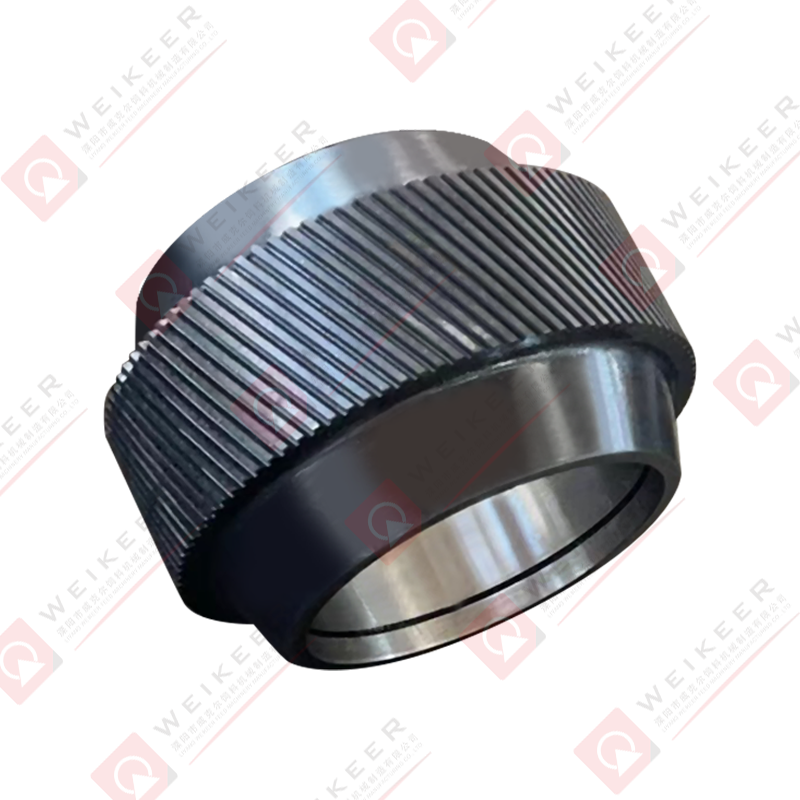
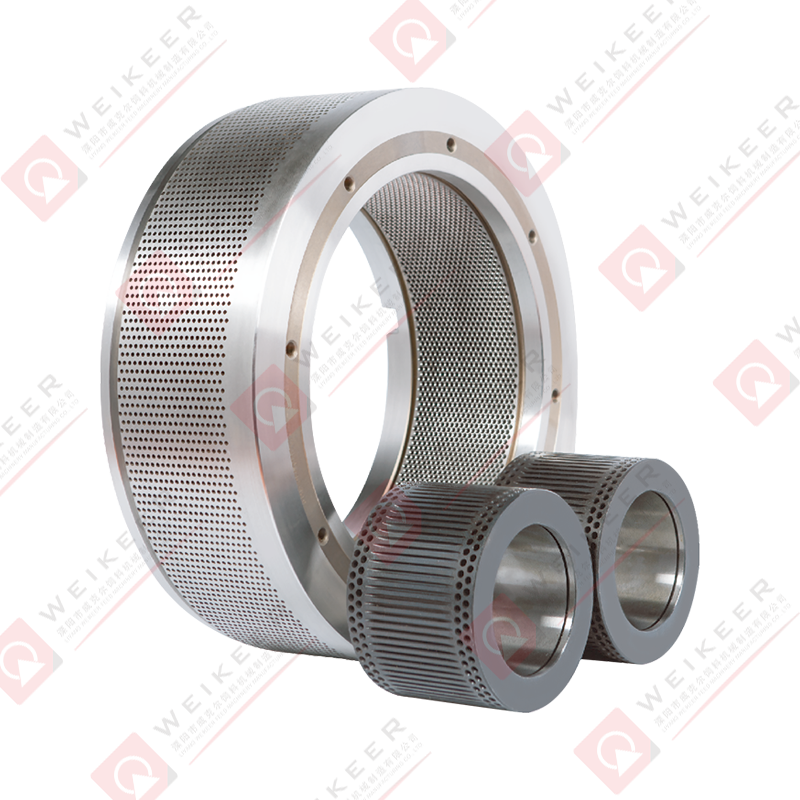
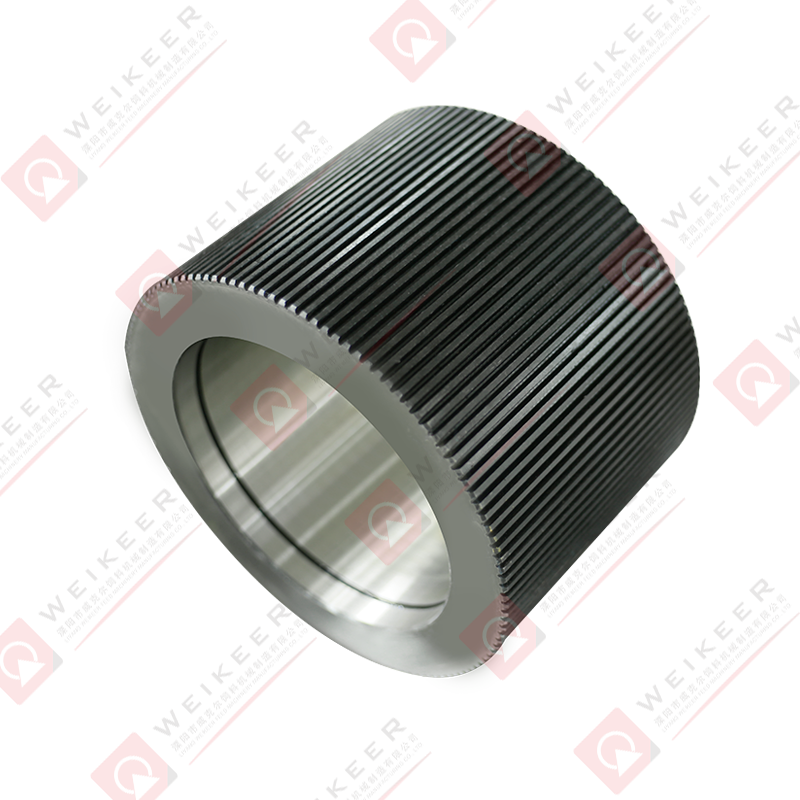
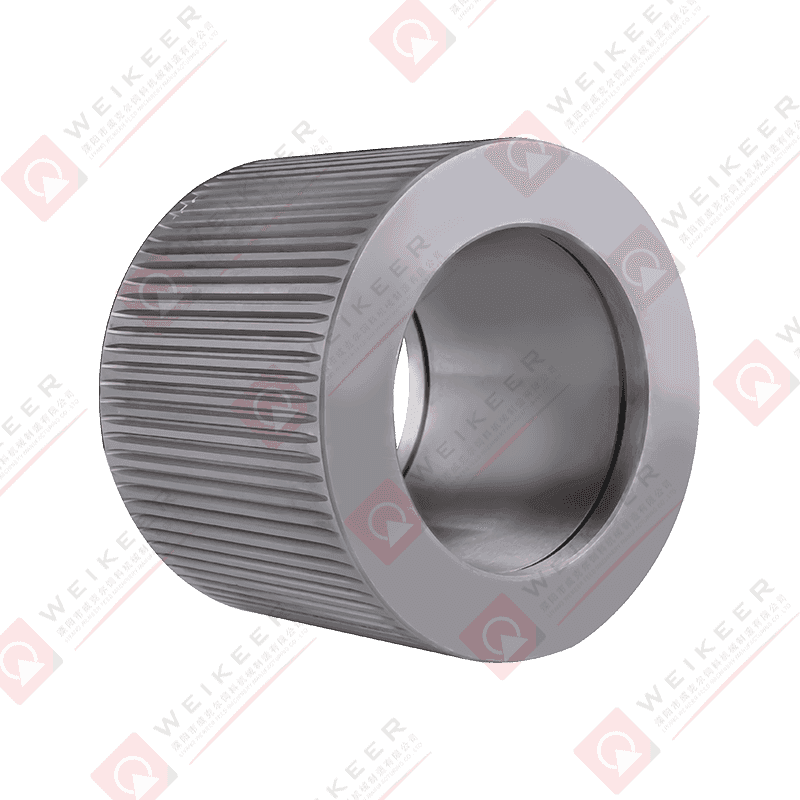
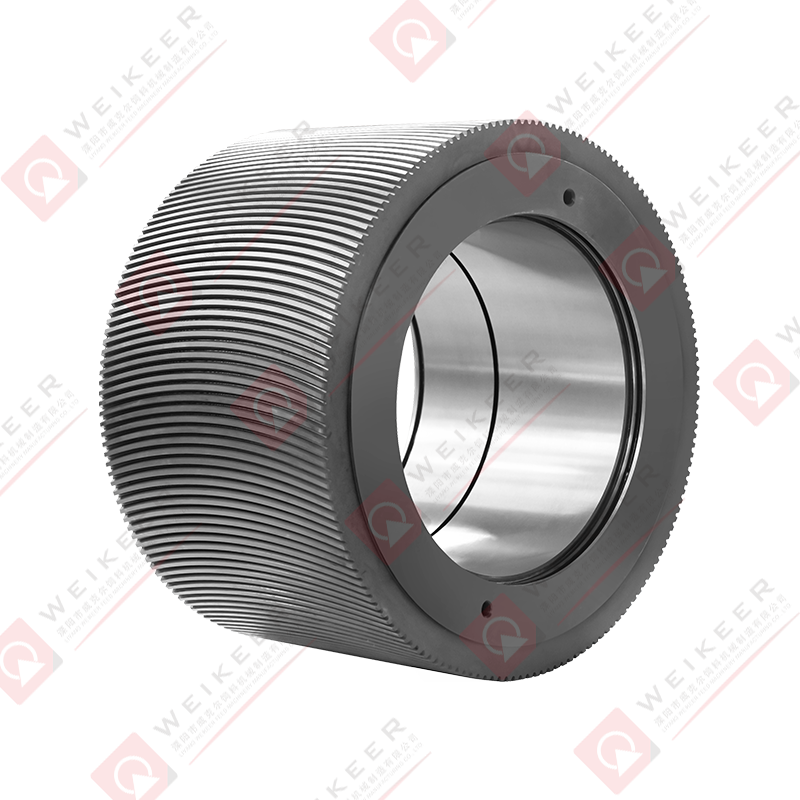
Pellet mills press roller shells are critical wear components in pelletizing systems used for animal feed, biomass, wood pellets, and industrial pellet production. These shells form the outer working surface of the press rollers and directly contact raw material and pellet dies during the compression process.
Because roller shells are subjected to high pressure, friction, and abrasive materials, their design, material selection, and surface pattern have a direct impact on pellet quality, production efficiency, and overall operating costs.
Function of Press Roller Shells in Pellet Mills
Press roller shells transmit force from the pellet mill rollers to the raw material, forcing it through the die holes to form uniform pellets. The shell surface grips and compresses the feedstock while maintaining consistent contact with the die surface.
A properly designed roller shell ensures stable material flow, reduces slippage, and improves pellet density. Worn or poorly matched shells can cause uneven feeding, reduced throughput, and excessive die wear.
Common Types of Roller Shell Surface Patterns
Roller shells are manufactured with different surface patterns to suit various materials and production goals. The correct pattern improves grip and compression efficiency.
Corrugated Roller Shells
Corrugated shells feature parallel grooves that provide strong grip and stable material feeding. They are commonly used in feed pellet production and are suitable for a wide range of raw materials.
Closed Groove Roller Shells
Closed groove designs create more aggressive compression, making them ideal for hard-to-pellet materials or high-density pellet requirements. They improve material capture and reduce slippage.
Open Groove Roller Shells
Open groove shells allow better material flow and are commonly used for softer feedstock. They help prevent material buildup and reduce heat generation.
Dimpled or Knurled Roller Shells
Dimpled and knurled patterns improve grip while minimizing material smearing. These patterns are often used for specialty feeds and certain biomass materials.
Materials Used for Roller Shell Manufacturing
Roller shells must withstand continuous abrasion, high contact stress, and thermal cycling. Material selection plays a major role in shell durability and cost efficiency.
- Alloy Steel: Provides good toughness and wear resistance for standard feed and biomass applications.
- High-Chromium Cast Iron: Excellent for abrasive materials due to superior hardness and wear resistance.
- Carburized Steel: Heat-treated for a hard surface layer and tough core for extended service life.
- Stainless Steel Alloys: Used in food-grade or corrosion-sensitive environments.
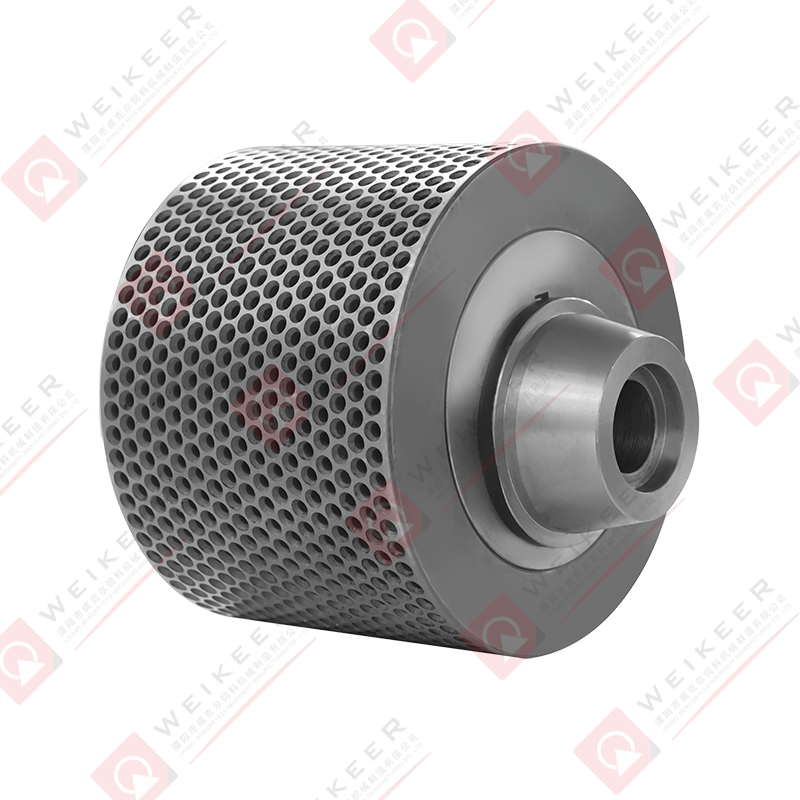
Key Factors Affecting Roller Shell Performance
Several operational and material factors influence how roller shells perform and how quickly they wear.
- Raw Material Abrasiveness: High mineral or sand content accelerates wear.
- Moisture Content: Improper moisture affects grip and increases slippage.
- Roller-Die Clearance: Incorrect gap leads to uneven loading and premature wear.
- Production Load: High throughput increases mechanical stress on shells.
- Lubrication and Bearing Condition: Poor bearing support increases shell vibration and wear.
Signs of Roller Shell Wear and Failure
Monitoring wear patterns helps operators replace shells before serious performance issues occur. Common wear symptoms include reduced pellet quality, increased energy consumption, and abnormal vibration.
- Flattened or rounded grooves reducing grip.
- Uneven wear across the shell surface.
- Cracks or surface spalling in hardened layers.
- Increased slippage and reduced pellet density.
How to Select the Right Roller Shells
Selecting the correct press roller shell is essential for optimizing pellet mill performance and minimizing operating costs. Selection should be based on material type, production goals, and equipment specifications.
Operators should match groove pattern, material hardness, and shell diameter to the specific pellet mill model and die configuration. Consulting with experienced suppliers helps ensure compatibility and performance.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures even loading and maximizes roller shell life. Incorrect mounting can lead to vibration, misalignment, and accelerated wear.
- Clean and inspect roller hubs before installing new shells.
- Ensure correct roller-die clearance according to manufacturer guidelines.
- Check bearing condition to prevent uneven shell loading.
- Run-in new shells at reduced load to allow proper seating.
Maintenance Strategies to Extend Shell Life
Preventive maintenance significantly extends the service life of press roller shells and reduces unplanned downtime. Routine inspection and proper operating practices are essential.
- Inspect groove condition and shell diameter regularly.
- Rotate or replace shells before severe wear develops.
- Control raw material quality to reduce abrasive contaminants.
- Maintain proper feeder and conditioner settings.
- Keep accurate wear and replacement records.
Impact on Pellet Quality and Production Efficiency
Press roller shell condition directly affects pellet durability, size consistency, and production throughput. Well-maintained shells provide stable compression, resulting in uniform pellet density and reduced fines.
Optimized roller shells also reduce energy consumption by minimizing slippage and unnecessary friction, improving overall mill efficiency and lowering production costs.
Conclusion
Pellet mills press roller shells are essential components that play a major role in pellet formation, production efficiency, and equipment longevity. Their surface pattern, material composition, and maintenance condition directly impact pellet quality and operating costs.
By selecting the correct roller shell design, following proper installation practices, and implementing a proactive maintenance program, pellet producers can achieve consistent pellet quality, extend equipment life, and maximize return on investment.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体