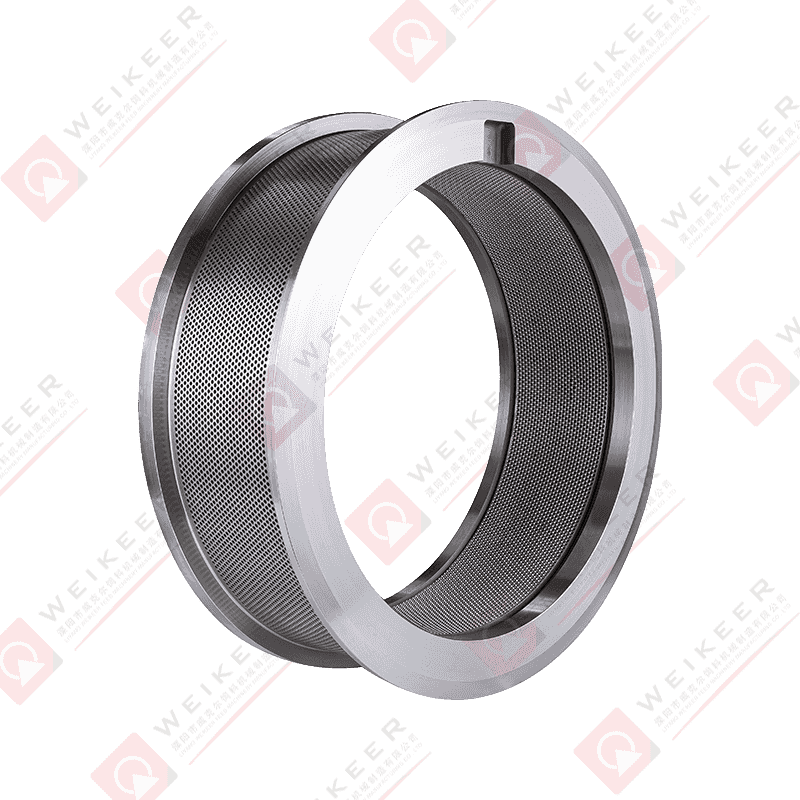
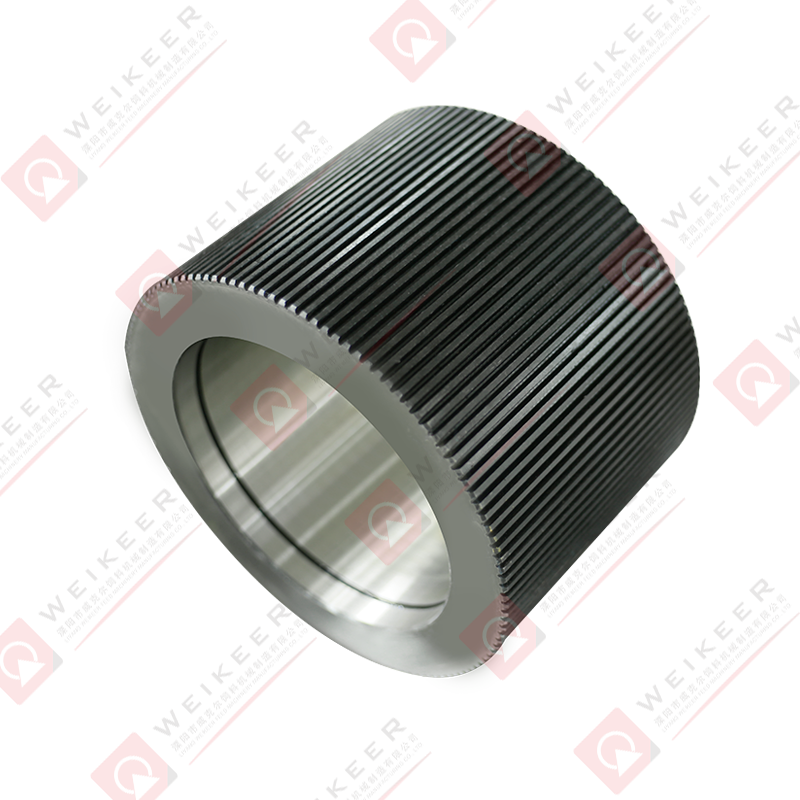
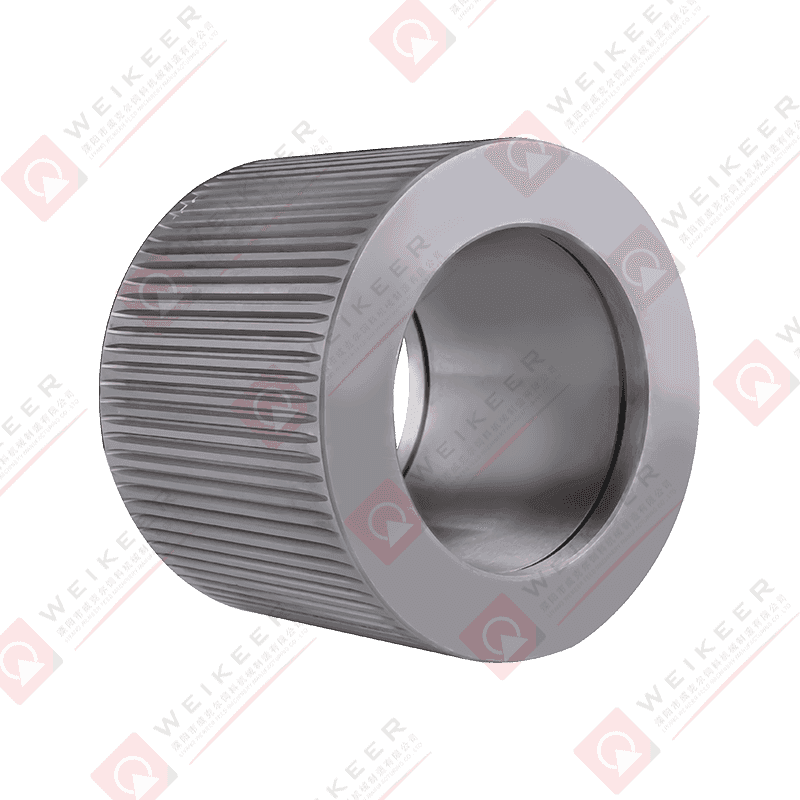
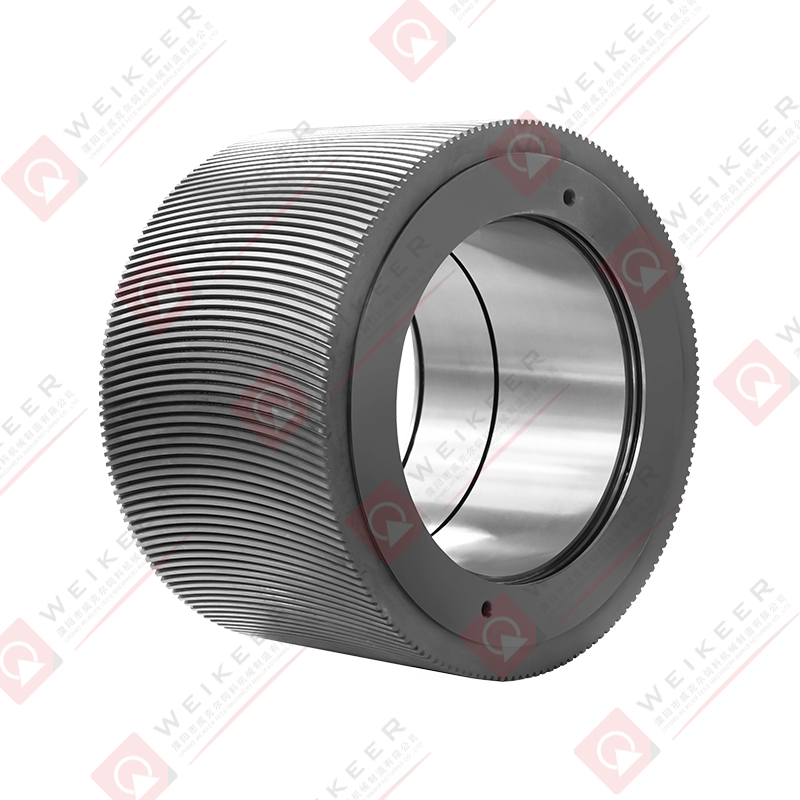
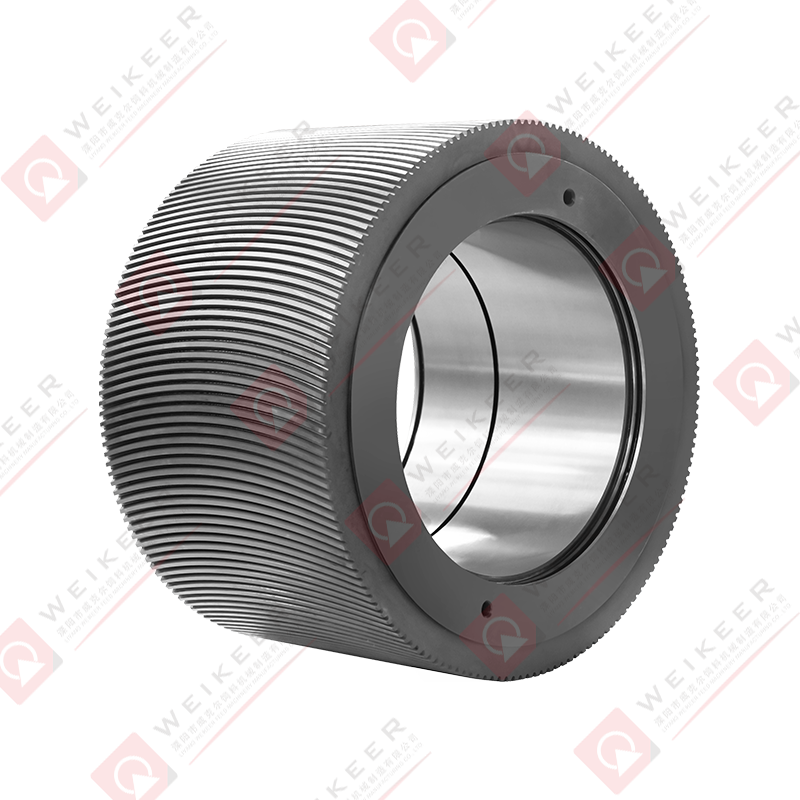
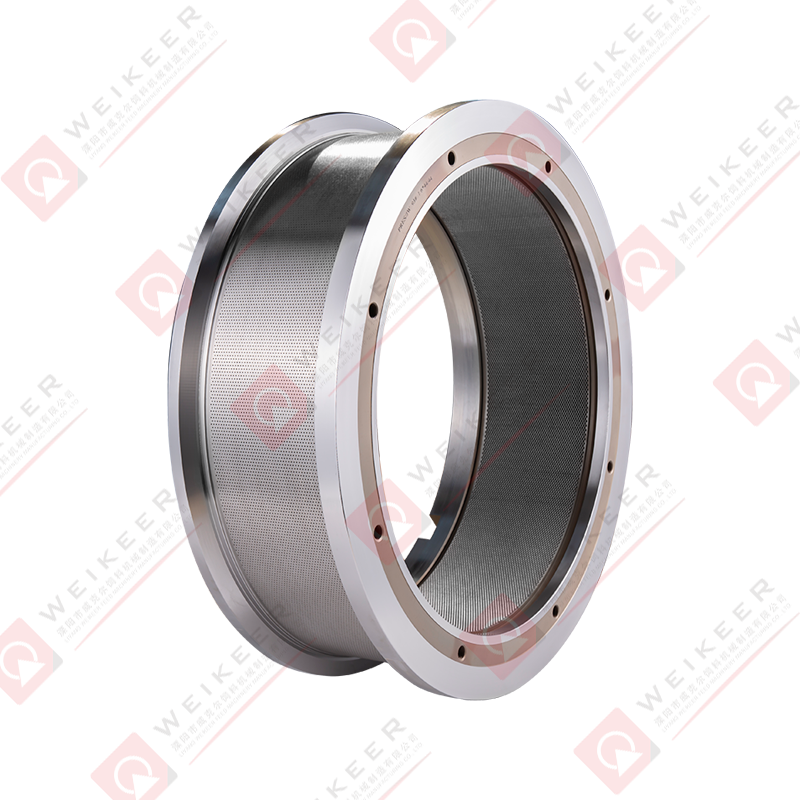
In the rapidly growing aquaculture industry, the production of high-quality fish feed is a critical factor that directly influences fish health, growth rates, and overall yield. One of the most essential components in this feed manufacturing process is the aqua feed pellet die . As a core part of the pelletizing system, the die plays a pivotal role in shaping raw ingredients into uniform, nutrient-rich pellets that meet the dietary needs of aquatic species.
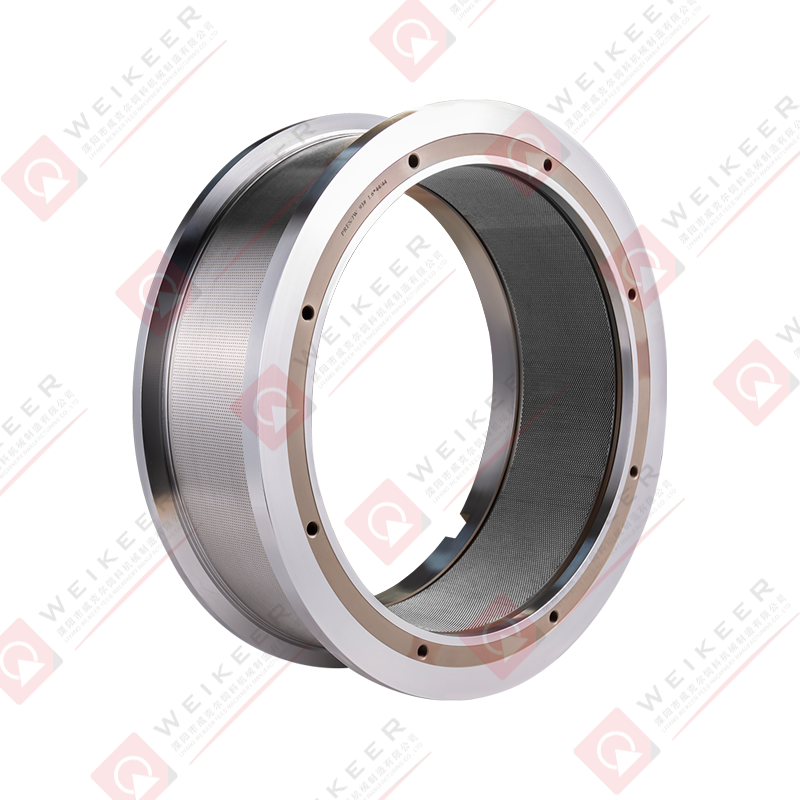
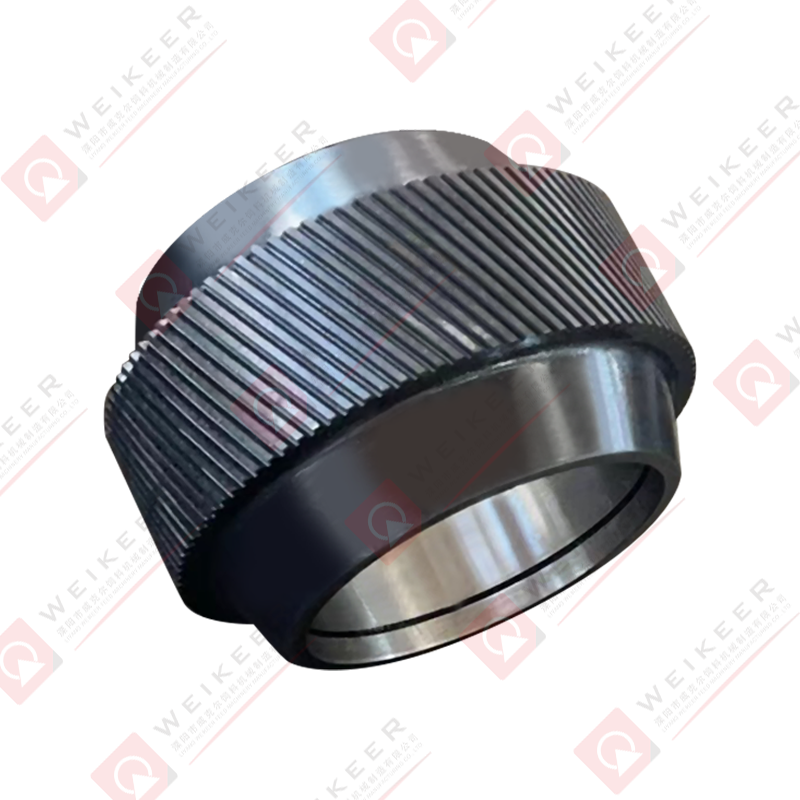
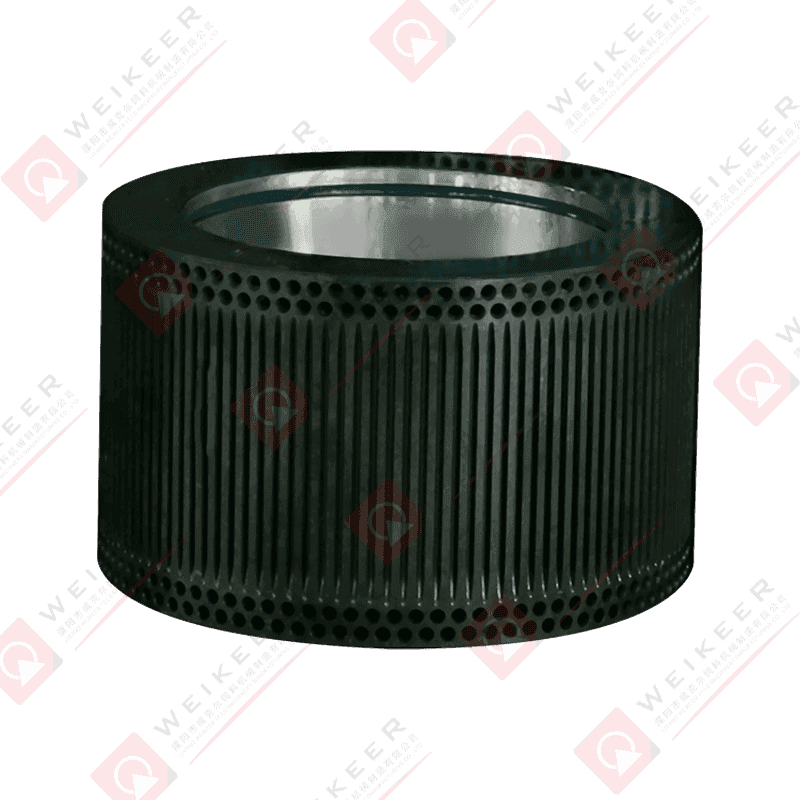
An aqua feed pellet die is a circular or flat metal plate with precision-drilled holes, used in pellet mills to compress and shape ground feedstock into pellets. During operation, the die rotates (or remains stationary depending on the mill type), while rollers press the feed material through the die’s holes under high pressure. The result is the formation of cylindrical pellets that are then cooled, dried, and packaged for use in fish farming.
These dies are specifically engineered for aquafeed production, where factors such as water stability, sinking or floating behavior, and digestibility are crucial. Depending on the target species—such as shrimp, salmon, tilapia, or trout—the specifications of the die, including hole size, diameter, compression ratio, and material composition, can be customized to produce pellets tailored to specific feeding behaviors and nutritional requirements.
Key Features of Aqua Feed Pellet Dies
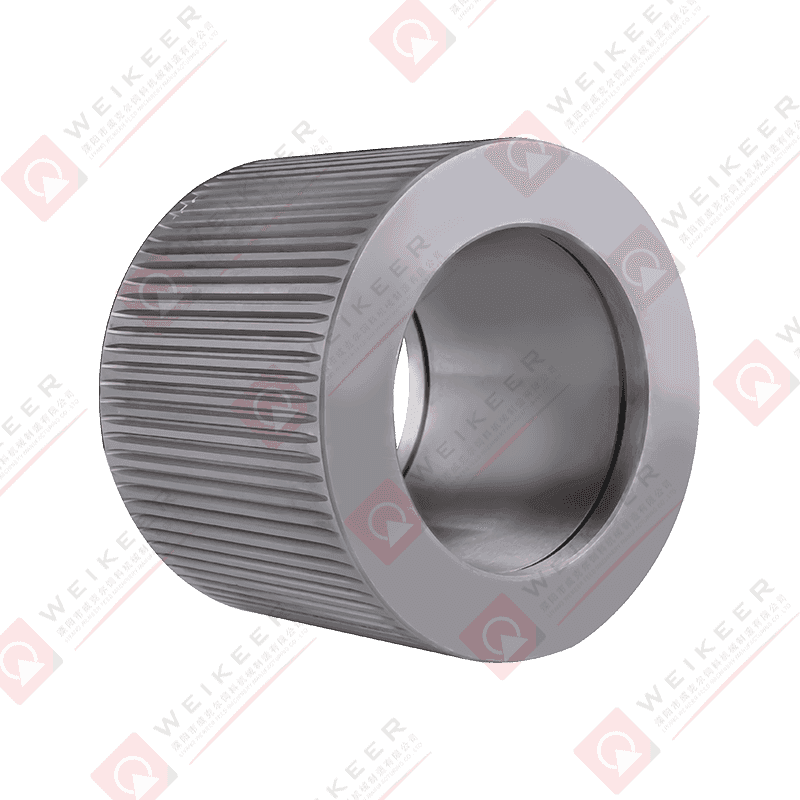
Material Quality:
High-grade alloy steel, stainless steel, or hardened carbon steel is commonly used to manufacture these dies. These materials offer superior wear resistance, ensuring longevity despite the abrasive nature of aquafeed ingredients like fish meal, soybean meal, and other fibrous components.
Compression Ratio:
This refers to the ratio between the depth of the entry zone and the effective thickness of the die. A higher compression ratio increases the density and durability of the pellets, which is particularly important for floating feeds designed to remain intact on the water surface for extended periods.
Die Diameter and Hole Size:
Dies come in various diameters and hole sizes, allowing manufacturers to produce pellets ranging from 0.8 mm to over 10 mm in diameter. Small holes are typically used for fry or small ornamental fish, while larger holes suit adult fish and crustaceans.
Surface Treatment:
Some dies undergo surface treatments like nitriding or chrome plating to enhance hardness and corrosion resistance, especially when producing feeds with high moisture or acidic components.
Importance in Aquaculture Feed Production
The aquafeed pellet die is not just a mechanical component—it's a determinant of product quality and production efficiency. Here’s why it matters:
Uniformity and Consistency: Properly designed dies ensure consistent pellet size and shape, which supports even nutrient distribution and efficient feeding practices.
Water Stability: For floating or slow-sinking feeds, the die influences how well the pellet maintains its structure in water, reducing waste and improving feed conversion ratios (FCR).
Throughput Efficiency: An optimized die design enhances the output capacity of the pellet mill, contributing to cost-effective mass production.
Energy Efficiency: Well-engineered dies reduce friction and power consumption during the pelleting process, lowering energy costs and environmental impact.
As global demand for seafood continues to rise and aquaculture intensifies, the need for reliable, high-performance aquafeed becomes more pressing. The aqua feed pellet die stands at the heart of this transformation, enabling the production of nutritionally balanced, durable, and species-specific fish feed. By investing in high-quality pellet dies and optimizing their use, feed manufacturers can significantly improve both productivity and sustainability in aquaculture operations.
In summary, while often overlooked, the aquafeed pellet die is a vital component that ensures the success of modern aquaculture by delivering feed that meets the precise biological and operational needs of fish farms around the world.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体