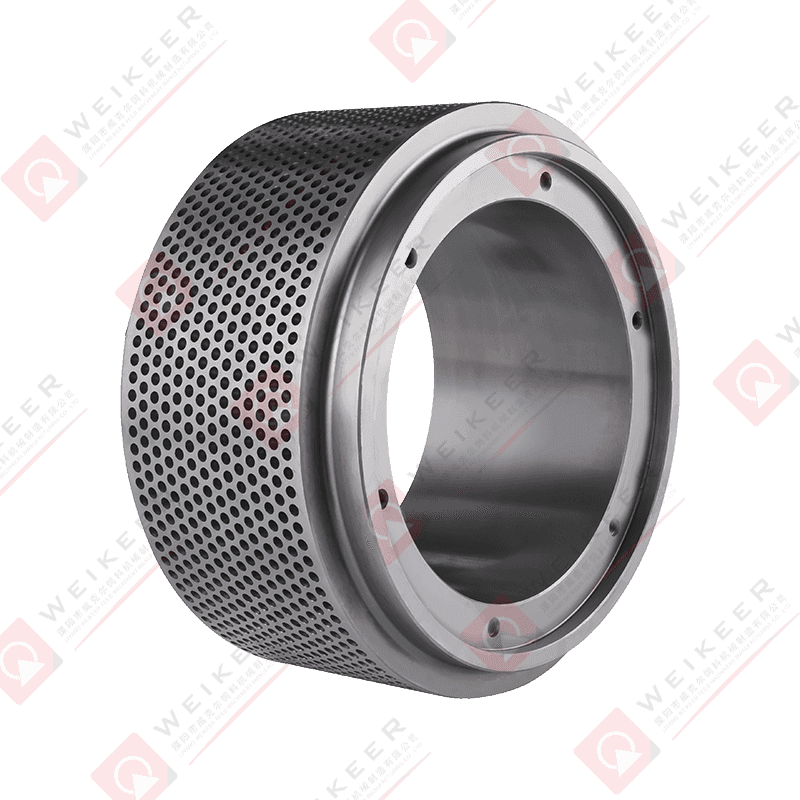
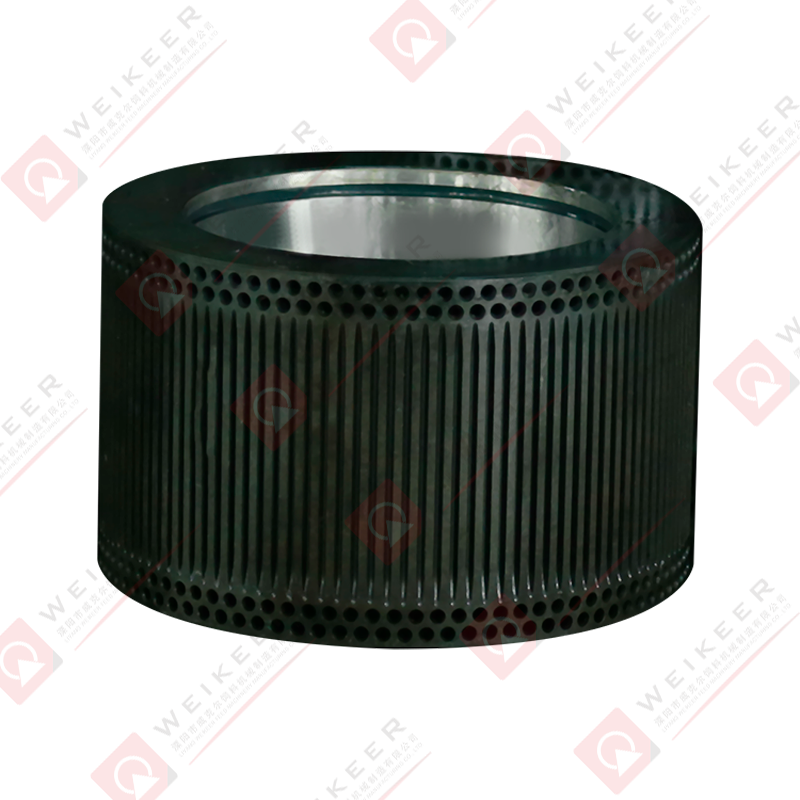
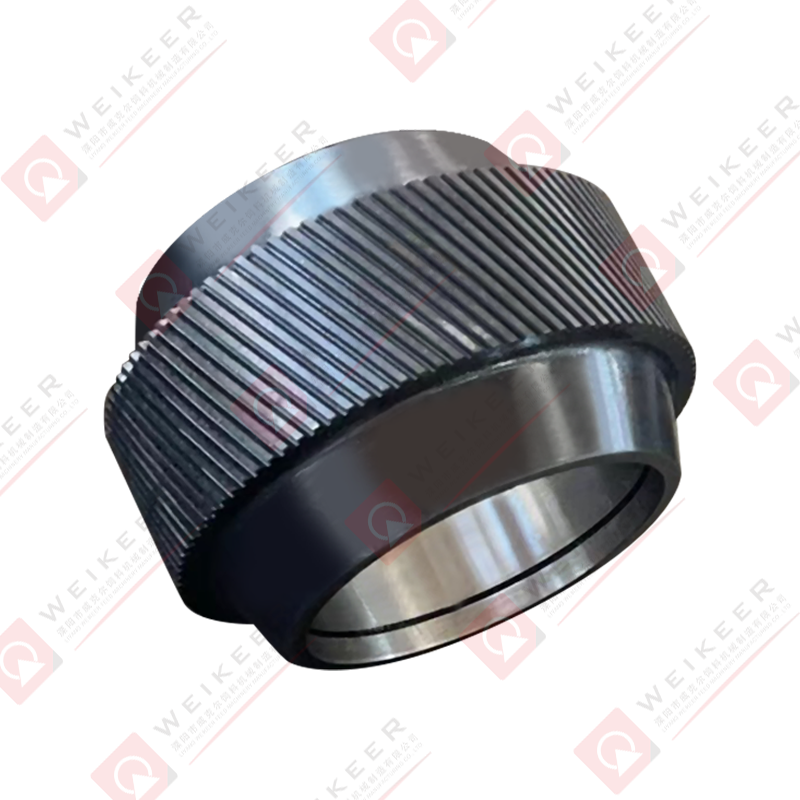
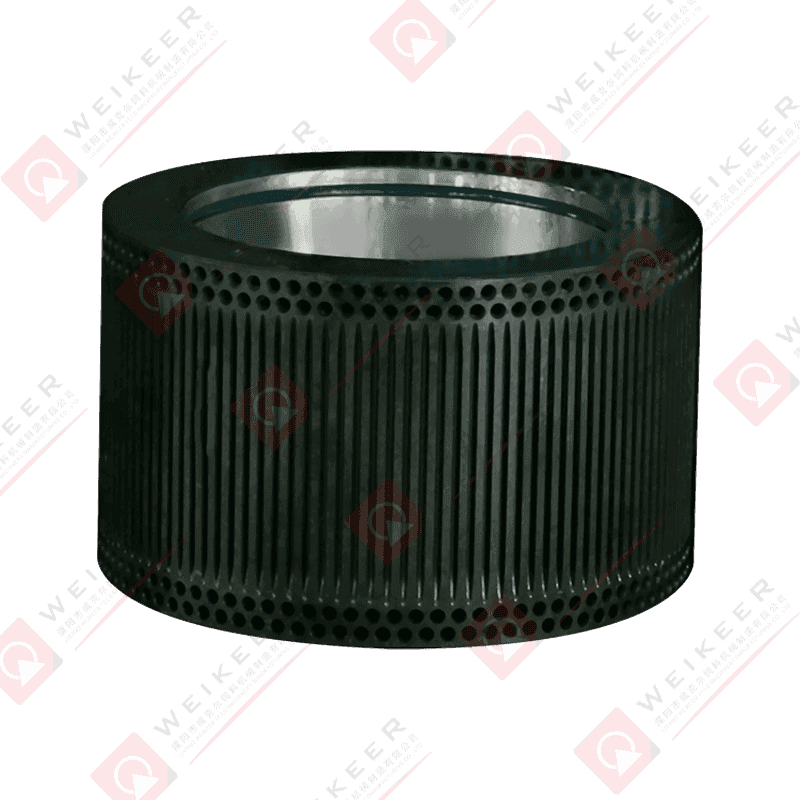
Understanding Stainless Steel Ring Die Performance Fundamentals
Stainless steel ring dies represent a significant investment in pellet mill operations, and optimizing their performance directly impacts production efficiency, product quality, and operational profitability. Unlike conventional alloy steel dies, stainless steel variants offer superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications involving moisture-rich formulations, marine environments, or products requiring stringent hygiene standards. The performance of these precision-engineered components depends on multiple interrelated factors including material specifications, geometric design, operating parameters, and maintenance practices. Understanding these fundamentals enables operators to maximize throughput while minimizing energy consumption and extending die service life.
The optimization process begins with recognizing that ring die efficiency is not a static characteristic but rather a dynamic relationship between the die, the pellet mill machinery, and the material being processed. Stainless steel dies, typically manufactured from grades such as AISI 304, 316, or specialized hardened variants like 420 or 440C, exhibit different performance characteristics compared to carbon steel alternatives. Their unique metallurgical properties influence heat dissipation, wear resistance, and material flow dynamics. Operators who understand these distinctions can implement targeted optimization strategies that leverage the specific advantages of stainless steel construction while mitigating potential limitations through proper configuration and operational adjustments.
Optimizing Die Specifications for Your Application
Hole Pattern Configuration and Distribution
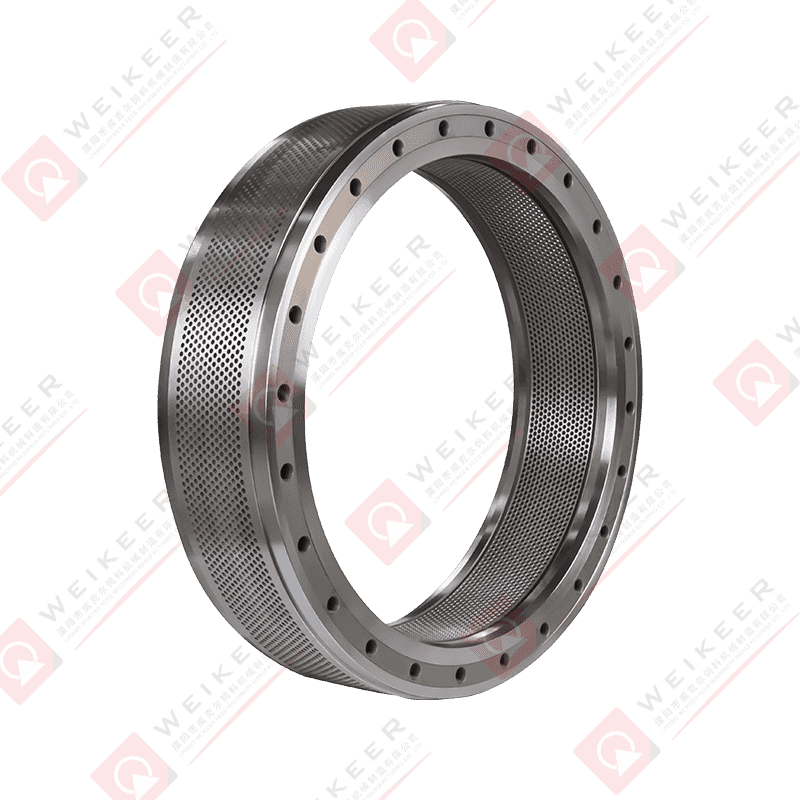
The hole pattern configuration on your stainless steel ring die significantly affects production efficiency and pellet quality. Optimal hole distribution ensures uniform material flow across the die surface, preventing overloading in specific areas while underutilizing others. Modern ring dies employ computer-optimized hole patterns that balance the effective working area with structural integrity requirements. For maximum efficiency, the hole pattern should provide 30-45% open area, depending on the material being pelleted. Higher open area percentages increase capacity but may compromise die strength, while lower percentages ensure durability at the expense of throughput. Analyze your production data to identify whether capacity or longevity is the limiting factor in your operation.
Compression Ratio Optimization
The compression ratio, defined as the effective length of the die channel divided by the hole diameter, represents one of the most critical parameters for optimization. Stainless steel dies with improper compression ratios waste energy through excessive resistance or produce inferior pellets due to insufficient compaction. For most feed applications, compression ratios between 1:8 and 1:12 provide optimal results, though specific formulations may require adjustments outside this range. High-fat or high-moisture formulations typically benefit from lower compression ratios (1:6 to 1:8), while dry or fibrous materials require higher ratios (1:10 to 1:13) to achieve adequate binding and pellet durability.
Relief and Counterbore Design
Advanced stainless steel ring dies incorporate relief holes and counterbore designs to optimize material flow and reduce back pressure. Relief holes, drilled at strategic angles, allow compressed air to escape during the pelleting process, reducing resistance and improving throughput by 10-15% compared to standard designs. Counterbores, which are enlarged sections at the die hole inlet, facilitate material entry and reduce wear at the critical inlet zone where friction is highest. When optimizing your die configuration, consider specifying these features for difficult-to-pellet formulations or high-capacity operations where every percentage point of efficiency improvement translates to significant production gains.
Conditioning Process Optimization for Ring Die Efficiency
The conditioning process preceding pelleting has profound effects on ring die performance and should be optimized in conjunction with die specifications. Proper conditioning gelatinizes starches, denatures proteins, and achieves optimal moisture and temperature levels that facilitate material flow through the die. For stainless steel ring dies, target conditioning temperatures between 75-90°C (167-194°F) for most feed applications, with moisture content adjusted to 15-17%. Under-conditioned material creates excessive friction within die holes, increasing power consumption, generating excessive heat, and accelerating wear. Conversely, over-conditioning can cause material to become sticky and adhere to die surfaces, reducing effective hole area and diminishing capacity.
Modern conditioning systems with multiple chambers and precise steam injection control enable fine-tuning of material properties before pelleting. Monitor conditioning performance by measuring material temperature and moisture at the conditioner outlet, adjusting steam flow and retention time to achieve consistent target values. The relationship between conditioning and die performance becomes particularly critical with stainless steel dies, as their thermal conductivity differs from carbon steel alternatives. Implement real-time monitoring of die temperature using infrared sensors, maintaining operating temperatures within manufacturer-specified ranges to prevent thermal degradation of the die material or excessive energy losses through heat dissipation.
Roller and Die Gap Adjustment for Peak Performance
The clearance between compression rollers and the ring die interior surface critically influences pelleting efficiency and die longevity. Optimal gap settings typically range from 0.1mm to 0.3mm (0.004-0.012 inches), though exact specifications depend on die diameter, roller diameter, and material characteristics. Insufficient clearance causes excessive friction, overheating, and rapid wear of both rollers and die. Excessive clearance allows material to slip between rollers and die without adequate compression, reducing capacity and producing poor-quality pellets with high fines content. Regular gap measurement and adjustment maintain peak efficiency throughout the die's service life.
| Die Diameter |
Optimal Gap Range |
Adjustment Frequency |
Expected Impact |
| 300-400mm |
0.1-0.2mm |
Every 500 hours |
5-10% capacity increase |
| 450-600mm |
0.15-0.25mm |
Every 400 hours |
8-12% capacity increase |
| 650-800mm |
0.2-0.3mm |
Every 300 hours |
10-15% capacity increase |
Implement a systematic approach to gap adjustment using precision measurement tools such as feeler gauges or dedicated gap measurement devices. Document gap measurements in a maintenance log, tracking changes over time to identify wear patterns and predict when roller or die replacement will be necessary. Many operators find that establishing a preventive adjustment schedule based on operating hours produces more consistent results than waiting for performance degradation to become apparent. For stainless steel dies, which may exhibit different wear characteristics than carbon steel alternatives, develop baseline data through careful monitoring during the initial operating period to establish optimal adjustment intervals specific to your operation.
Lubrication Strategies for Stainless Steel Ring Dies
Proper lubrication significantly enhances stainless steel ring die efficiency by reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing material buildup within die holes. Unlike external lubricants applied to machinery, die lubrication involves incorporating specific ingredients into the feed formulation or applying specialized conditioning agents. Molasses, vegetable oils, and specialized pellet binders serve dual purposes as nutritional components and pelleting aids. For maximum efficiency, target 2-4% added fat in feed formulations, with the specific level optimized based on ingredient composition and desired pellet characteristics.
The lubrication effect varies depending on when and how fats are introduced. Post-pellet oil application, while beneficial for dust control and energy density, provides no lubrication benefit during the pelleting process. For optimal die performance, incorporate at least 1-2% fat in the pre-pellet mixture, reserving additional fat for post-pellet application if formulation requirements dictate higher total fat levels. Monitor the relationship between fat content and specific energy consumption (kWh per ton produced), identifying the optimal level that minimizes energy use while maintaining pellet quality standards. Stainless steel dies may require slightly different lubrication strategies compared to carbon steel alternatives due to differences in surface characteristics and friction coefficients.
Implementing Preventive Maintenance Programs
Systematic preventive maintenance maximizes stainless steel ring die efficiency and service life while minimizing unexpected downtime. Develop a comprehensive maintenance schedule encompassing daily, weekly, and monthly activities tailored to your specific operating conditions and production volume. Daily tasks should include visual inspection for damage or unusual wear patterns, verification of proper operating temperature ranges, and monitoring of power consumption trends that may indicate developing problems. Weekly activities encompass more detailed inspections, gap measurements, and cleaning procedures to remove accumulated material from die surfaces and holes.
- Conduct monthly dimensional verification of critical die specifications using precision measuring instruments to track wear progression and plan timely replacement
- Implement die rotation schedules for operations with multiple dies, distributing operating hours evenly to maximize total productive life across your die inventory
- Establish baseline performance metrics including specific energy consumption, production rate, and pellet quality parameters for comparison during routine assessments
- Document all maintenance activities, observations, and measurements in detailed records that enable trend analysis and predictive maintenance strategies
- Schedule professional die inspections and potential reconditioning at manufacturer-recommended intervals, typically after 2000-4000 operating hours depending on application severity
Optimizing Operational Parameters Through Data Analysis
Modern pellet mill operations benefit tremendously from systematic data collection and analysis to optimize ring die performance. Implement monitoring systems that track key performance indicators including production rate, specific energy consumption (kWh/ton), pellet durability index, fines percentage, die temperature, and motor amperage. Analyze these parameters collectively rather than in isolation, as changes in one variable often affect others. For example, increasing production rate by adjusting feeder speed may initially appear beneficial but could increase energy consumption and reduce pellet quality if conditioning and die capacity are insufficient to handle the increased throughput.
Establish target ranges for each monitored parameter based on your specific equipment, formulations, and quality requirements. Use statistical process control techniques to identify when parameters drift outside acceptable ranges, triggering investigation and corrective action before significant problems develop. Advanced operations implement real-time optimization algorithms that automatically adjust conditioning temperature, steam flow, and feed rate to maintain optimal efficiency as raw material characteristics vary. Even without sophisticated automation, manual analysis of production data collected at regular intervals enables continuous improvement through incremental adjustments that collectively yield substantial efficiency gains.
Die Break-In and Seasoning Procedures
New stainless steel ring dies require proper break-in procedures to achieve optimal efficiency and develop the polished internal surface finish that facilitates material flow. The break-in period typically spans 8-12 operating hours, during which production capacity gradually increases as die holes become properly conditioned. Begin break-in with formulations containing higher fat content (3-4%) and optimal conditioning to minimize friction and wear during this critical initial operating phase. Avoid running at maximum capacity during break-in, instead targeting 70-80% of rated throughput to allow gradual development of proper working surfaces.
Monitor die temperature closely during break-in, as stainless steel's thermal properties may result in different heat generation and dissipation patterns compared to carbon steel dies. Expect power consumption to be 10-15% higher during initial operation, gradually decreasing as the die becomes properly seasoned. Some operators accelerate the break-in process by running dedicated seasoning formulations with enhanced lubrication properties before transitioning to standard production formulas. Document break-in performance metrics to establish baseline data for future comparison, enabling early detection of problems should performance degrade unexpectedly during normal operation.
Troubleshooting Common Efficiency Problems
Even well-maintained stainless steel ring dies occasionally experience efficiency problems requiring systematic troubleshooting to identify and resolve root causes. High specific energy consumption, the most common efficiency complaint, typically results from excessive die-roller clearance, inadequate conditioning, improper compression ratio, or worn die holes. Begin troubleshooting by verifying that conditioning parameters meet target specifications, as under-conditioned material creates excessive friction regardless of die condition. Next, check die-roller clearance and adjust if necessary, as this represents the most frequent cause of efficiency loss in otherwise properly configured systems.
Capacity limitations below rated specifications suggest material flow restrictions, often caused by hole blockage, inadequate effective working area, or formulation characteristics incompatible with current die configuration. Inspect die holes for partial blockage by hard material deposits or glazed surfaces that impede flow. Clean thoroughly using appropriate mechanical or chemical methods, avoiding aggressive techniques that might damage the precision-drilled holes or compromise the stainless steel surface. If capacity problems persist after cleaning and gap adjustment, consider whether die specifications properly match your formulation characteristics, potentially requiring a different compression ratio or hole pattern to achieve rated performance.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Optimization Investments
Optimization efforts require investment in monitoring equipment, maintenance procedures, and potentially upgraded die specifications, making cost-benefit analysis essential for prioritizing improvement initiatives. Calculate the potential savings from efficiency improvements by quantifying current specific energy consumption and production rates, then modeling the impact of proposed optimizations. A 5% reduction in specific energy consumption in a facility producing 50,000 tons annually at $0.12/kWh electricity cost saves approximately $15,000-$20,000 annually, easily justifying modest investments in gap measurement tools, conditioning system upgrades, or premium die specifications.
Beyond direct energy savings, optimization improvements affect multiple cost centers including reduced die replacement frequency, improved pellet quality reducing customer complaints, increased production capacity enabling revenue growth, and decreased maintenance labor through more predictable equipment performance. Develop comprehensive ROI calculations that capture these broader benefits rather than focusing solely on energy consumption. Most optimization initiatives targeting stainless steel ring die performance achieve payback periods under 12 months, with benefits continuing throughout the die's service life and establishing operational best practices that improve overall facility efficiency beyond the specific ring die application.
Maximizing stainless steel ring die efficiency requires a systematic approach encompassing proper specification selection, optimal operating parameter configuration, rigorous maintenance procedures, and continuous performance monitoring. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, pellet mill operators can achieve substantial improvements in production efficiency, energy consumption, product quality, and equipment longevity, directly contributing to enhanced profitability and competitive advantage in increasingly demanding markets.


 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى 中文简体
中文简体